ESOP Taxation in India 2025 – Income Tax Rules for Startups & Employees Simplified
Learn how ESOPs are taxed in India in 2025. Know about deferment for eligible startups, taxation at two stages, latest income tax sections like 17(2), 115BAC, and relevant CBDT notifications explained in easy terms.
Table of Contents
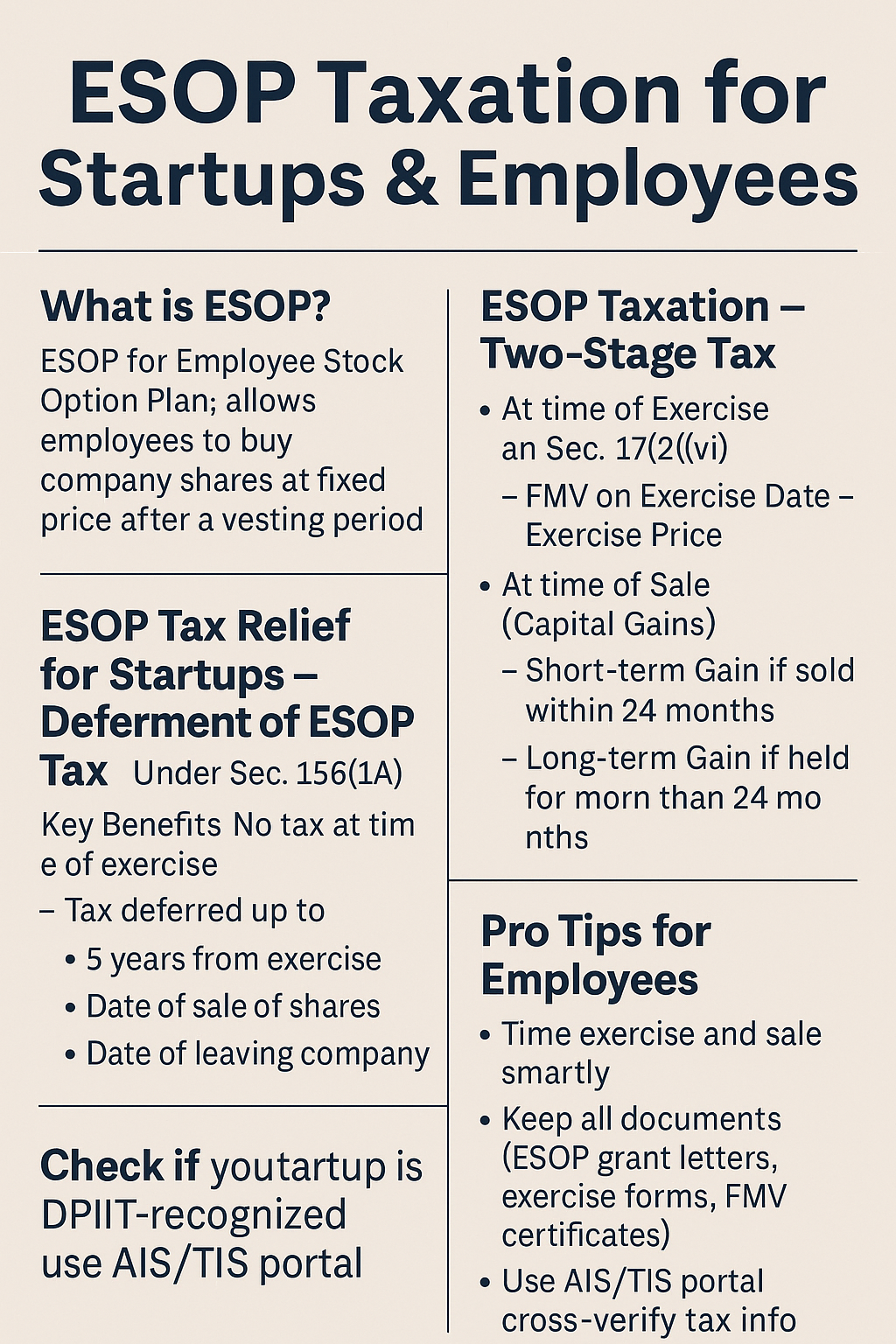
What is ESOP?
ESOP stands for Employee Stock Option Plan – it allows employees to buy company shares at a fixed price (called exercise price) after a certain period (called vesting period). Startups use ESOPs to attract and retain talent without paying high salaries.
Why Startups Use ESOP?
- To reward loyal employees
- To give a sense of ownership
- To save cash salary
- To boost productivity and retention
Popular among tech startups, ESOPs help align the employee’s goals with the company’s success.
ESOP Taxation in India (2025) – Two-Stage Tax
ESOPs are taxed at two stages:
Stage 1: At the Time of Exercise
- When? When the employee chooses to exercise the option and buys shares.
- Tax? Perquisite under Section 17(2)(vi) of the Income Tax Act.
- How Calculated?
FMV on Exercise Date – Exercise Price = Perquisite Value
This value is added to salary income and taxed as per your income tax slab.
Example:
- FMV = ₹500
- Exercise Price = ₹100
- Perquisite = ₹400
If 1000 shares exercised → ₹4,00,000 is taxable under salary.
Stage 2: At the Time of Sale (Capital Gains)
- When? When the employee sells the ESOP shares.
- Tax? Capital Gains Tax under Section 45.
- Type of Gain:
- Short-term (if sold within 24 months of exercise)
- Long-term (if held for more than 24 months)
| Holding Period | Type | Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| < 24 months | Short-term | As per slab |
| > 24 months | Long-term | 20% with indexation |
Special Tax Relief for Startups – Deferment of ESOP Tax
Startups recognized by DPIIT can defer the Stage 1 tax under Section 156(1A) (Notification No. GSR 127(E) dated 19.02.2020).
Key Benefits:
- No tax at the time of exercise.
- Tax deferred up to:
- 5 years from exercise, or
- Date of sale of shares, or
- Date of leaving the company
Whichever is earlier
This was introduced to solve the “tax on paper gain” issue when employees exercise shares but can’t sell due to lock-in or unlisted company.
Important: To avail deferment:
- Company must be DPIIT recognized startup
- Employee must file Form 12BA & Form 12BB
- Employer must withhold and report in Form 16 & Form 24Q
Relevant Income Tax Sections & Notifications
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| 17(2)(vi) | ESOP perquisite included in salary |
| 192(1C) | TDS for eligible startups on deferred tax |
| 115BAC | New tax regime – affects deductions, includes ESOP |
| 156(1A) | Deferment of tax for eligible startups |
| Notification GSR 127(E) | CBDT notification on ESOP tax deferment (Feb 2020) |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Not accounting FMV properly
- Get a CA valuation report for unlisted shares
- Ignoring tax at exercise
- Even if you didn’t sell shares, exercise triggers tax unless deferred
- Wrong reporting in ITR
- Declare salary + capital gains properly
Pro Tips for Employees
- Time your exercise and sale smartly
- Keep all ESOP grant letters, exercise forms, FMV certificates
- Check if your startup is DPIIT-recognized for deferment benefit
- Use AIS/TIS portal to cross-verify tax info
Final Conclusion
ESOPs are a powerful wealth-building tool, but taxation can be tricky. Understanding the two-stage tax, deferment options for startups, and proper documentation is key. Consult a tax expert if you plan to exercise or sell a large ESOP allotment in FY 2025–26.
Useful Links:
Visit Taxgiveindia.com for filing returns & other services.